Art Modern (1935-1950)
History
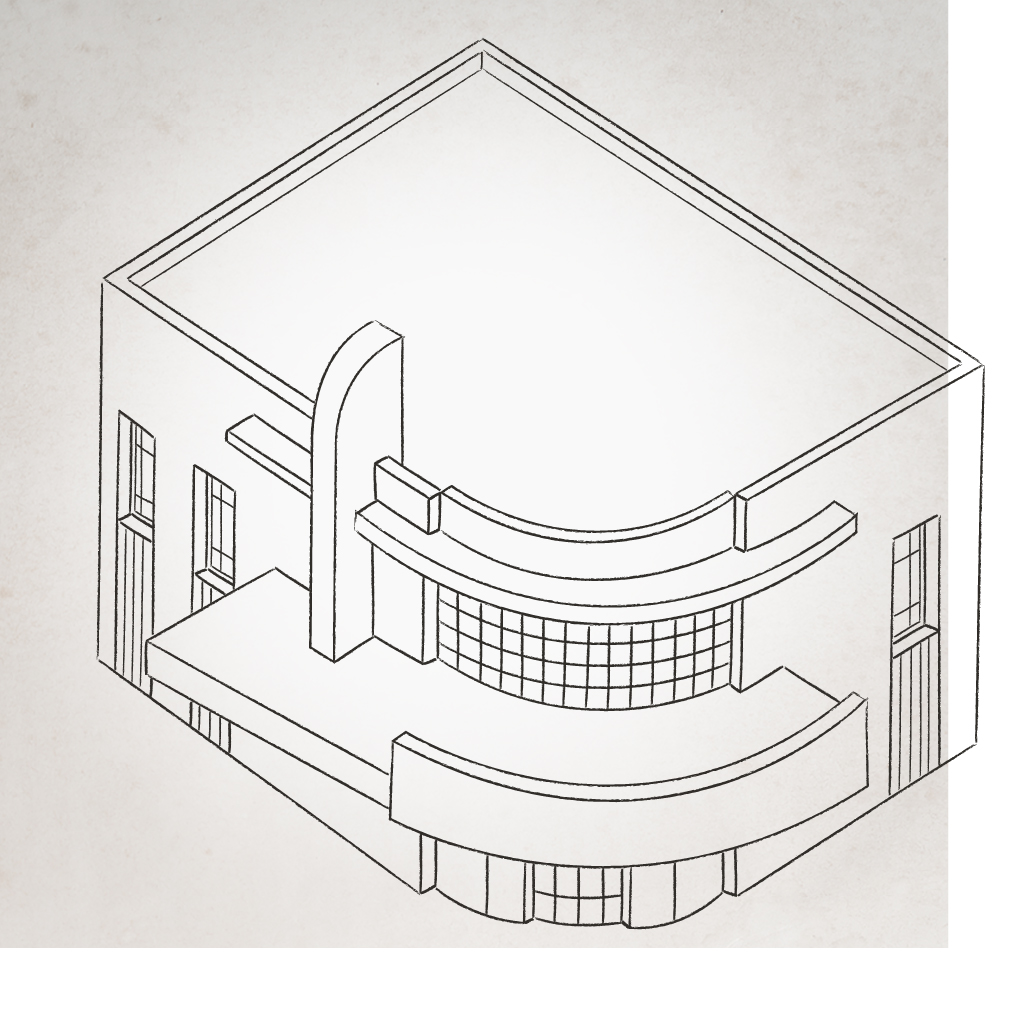
Like Art Deco style, and sometimes combined with it, Art Modern was a part of the Modern movement and the rejection of historical styles. While the style is an economical one, popularized during the Great Depression, it was meant to represent the dynamic progress of the 20th century and was highlighted at the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair. Its inspiration comes from the machine aesthetic of the period’s industrial design, especially that of the railway car, motorcar and steamship. Hence it is a very streamlined style, giving a sense of speed and motion.